SAP
What Is a Production Order? A Production Order in SAP is a formal instruction to manufacture a specific quantity of materials within a set timeframe….

In SAP systems, especially within Defense Forces & Public Security (DFPS) solutions, 0DF_PONUM plays a critical role in identifying and managing purchase orders across the…
Once a repair is complete and the customer has approved the quotation or fixed price, SAP generates a billing document to finalize the financial side…

Purchase Requisition in SAP Supply Planning In SAP, a Purchase Requisition is an internal request to the purchasing team to source specific materials or services…
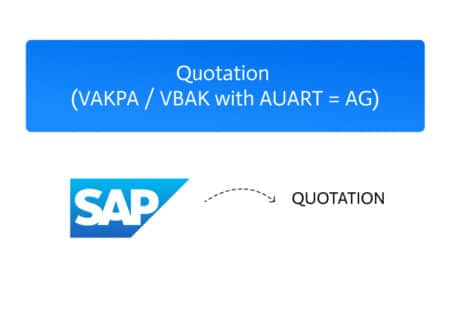
In SAP’s In-House Repair process, quotations are used when a customer must first approve repair costs before any service begins. This step ensures transparency and…